Subvolumes
This section covers managing Subvolume Groups and individual Subvolumes for organizing and controlling access to storage within a larger volume.
Accessing Subvolumes
To access the Subvolume section:
- Go to Sidebar Menu ➝ Click on Volumes ➝ Select Subvolume Group or Subvolumes
Subvolume Groups
Overview
The Subvolume Group interface allows users to:
- Create logical groupings of subvolumes.
- Allocate space and assign access permissions.
- Edit or delete existing groups.
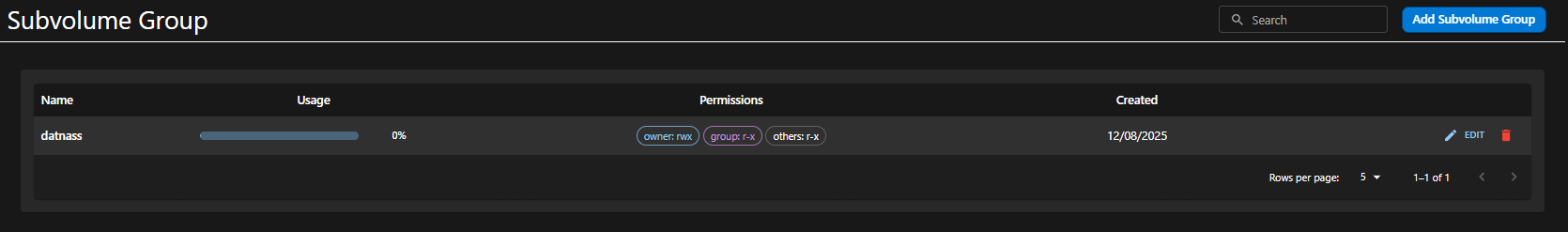
Subvolume Group List View
The main table provides a summary of existing Subvolume Groups:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of the subvolume group |
| Usage | Shows the storage usage percentage |
| Permissions | Displayed for Owner, Group, and Others (e.g., rwx, r-x) |
| Created | Creation date of the group |
| Actions | ✏️ Edit and 🗑️ Delete buttons available for each group |
Click “Add Subvolume Group” (top-right) to create a new one.
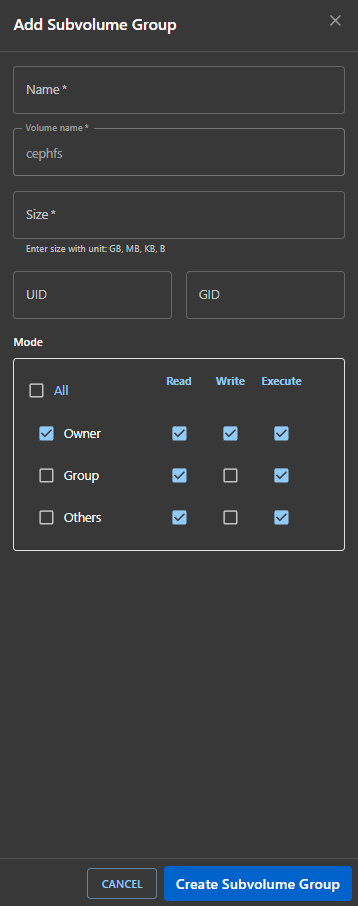
Creating a Subvolume Group
Click on Add Subvolume Group to open the creation form.
Fields
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Unique name for the group |
| Volume name | Select associated volume (e.g., cephfs) |
| Size | Assign size using units like GB, MB, KB |
| UID / GID | Set user/group IDs (optional) |
Permissions (Mode Section)
Set read/write/execute access for:
- ✅ Owner
- ✅ Group
- ✅ Others
- ✅ All (applies to everyone)
Buttons
- 🔵 Create Subvolume Group – to save.
- ⚪ Cancel – to discard the operation.
Editing a Subvolume Group
Click the ✏️ Edit button in the list view.
Edit the following:
- Name, Size, UID/GID, and Permissions.
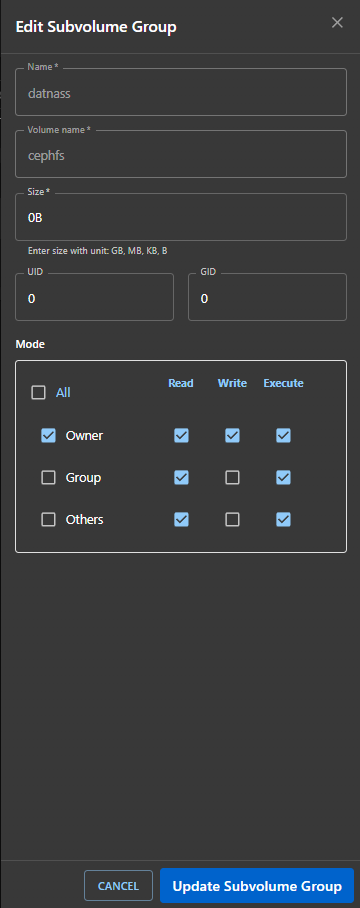
Click Update Subvolume Group to save changes.
Deleting a Subvolume Group
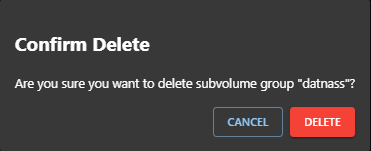
Click the 🗑️ Delete icon. A confirmation modal will appear.
Subvolumes
Overview
The Subvolumes page allows users to manage individual subvolumes under specific subvolume groups. Subvolumes are logical units used for organizing and controlling access to storage within a larger volume (e.g., cephfs).
Users can create, edit, and delete subvolumes, define their sizes, ownership, and set access permissions.
Accessing the Subvolumes Page
To navigate to the Subvolumes section:
- In the left sidebar, click on “Volumes”.
- Select “Subvolumes”.
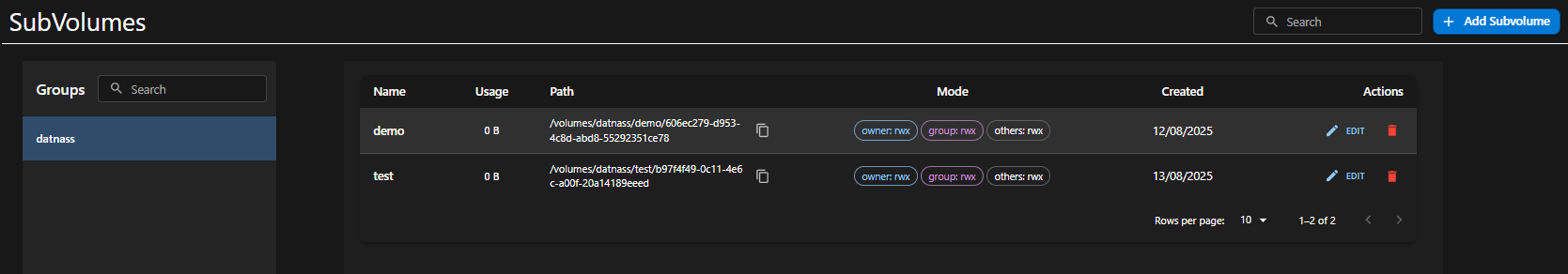
Subvolumes Interface Overview
The page is split into two panels:
- Left Panel (Groups): Displays available Subvolume Groups (e.g.,
datnass). Select a group to view its subvolumes. - Right Panel (Subvolumes): Displays subvolumes under the selected group.
Columns Displayed
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Subvolume name |
| Usage | Current used storage |
| Path | Auto-generated full path of the subvolume |
| Mode | Permissions (owner, group, others) |
| Created | Date of creation |
| Actions | Edit or delete subvolume |
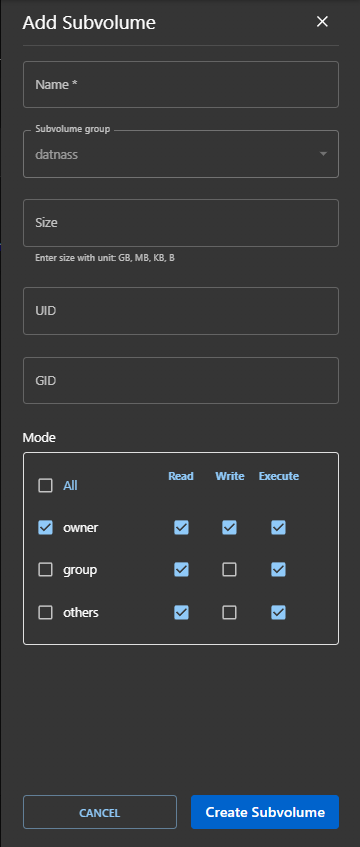
Add a Subvolume
To create a new subvolume:
- Click the "+ Add Subvolume" button (top-right).
- Fill in the following fields:
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Yes | Unique name for the subvolume |
| Subvolume Group | Yes | Select the group to which this subvolume belongs |
| Size | Yes | Enter storage size (e.g., 10GB, 500MB) |
| UID / GID | No | Optional Unix user/group IDs |
| Mode | No | Set read/write/execute permissions for Owner, Group, and Others |
- Click “Create Subvolume”.
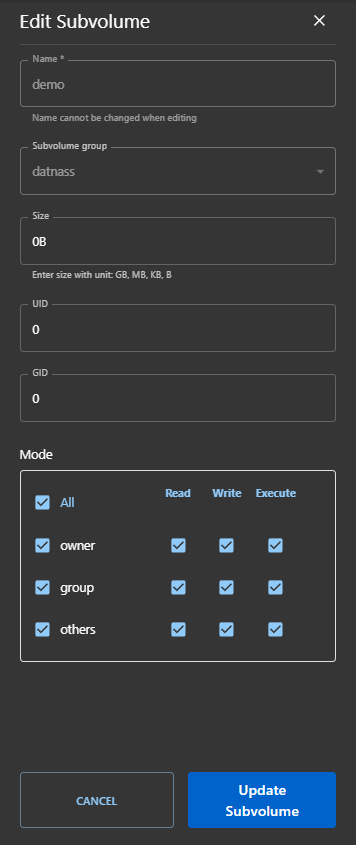
Edit a Subvolume
To modify an existing subvolume:
- Click the Edit icon (pencil) in the Actions column.
- You can update:
- Size
- Permissions
- UID / GID
- The name cannot be changed once created.
- Click “Update Subvolume”.
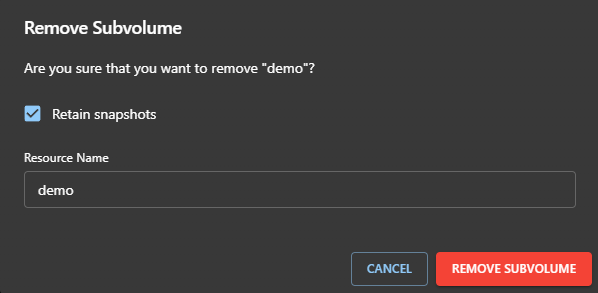
Delete a Subvolume
To delete a subvolume:
- Click the red trash icon in the Actions column.
- In the confirmation dialog:
- Verify the Resource Name to ensure you are deleting the correct subvolume.
- (Optional) Check Retain snapshots if you want to keep the snapshots of the subvolume while deleting the main resource.
- Click REMOVE SUBVOLUME to confirm deletion, or CANCEL to abort.
Permissions Reference
Permissions control the access levels for different user types:
| Target | Description |
|---|---|
| Owner | The user who owns the subvolume |
| Group | Users in the same group |
| Others | All other users |
Permission Types
| Permission | Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Read | r | Can view/list files |
| Write | w | Can add/modify files |
| Execute | x | Can execute/run files or enter directories |
Permission Examples
| Permission String | Description |
|---|---|
rwx | Full access |
r-x | Read and execute only |
--x | Execute only |
owner: rwx, group: rwx, others: rwx | Full access for all |
owner: rwx, group: r-x, others: r-- | Restricted access |